Do you know the 7 Silage Sins?
- 7 Jun 2021
- 0 Comments

When it comes to producing good quality, nutritious silage small things can make a big difference. This is especially true of mistakes. A shortcut or a small oversight can ultimately result in silage that is unusable due to insufficient dry matter content or worse, silage that is dangerous to herd health because of mould growth and the likely presence of mycotoxins or Listeria.
Many farmers have come to accept some issues, particularly with mould, as inevitable and as a necessary evil. The reality is however, it's all too often caused by someone committing one of a number of silage "sins".
So what are these sins?
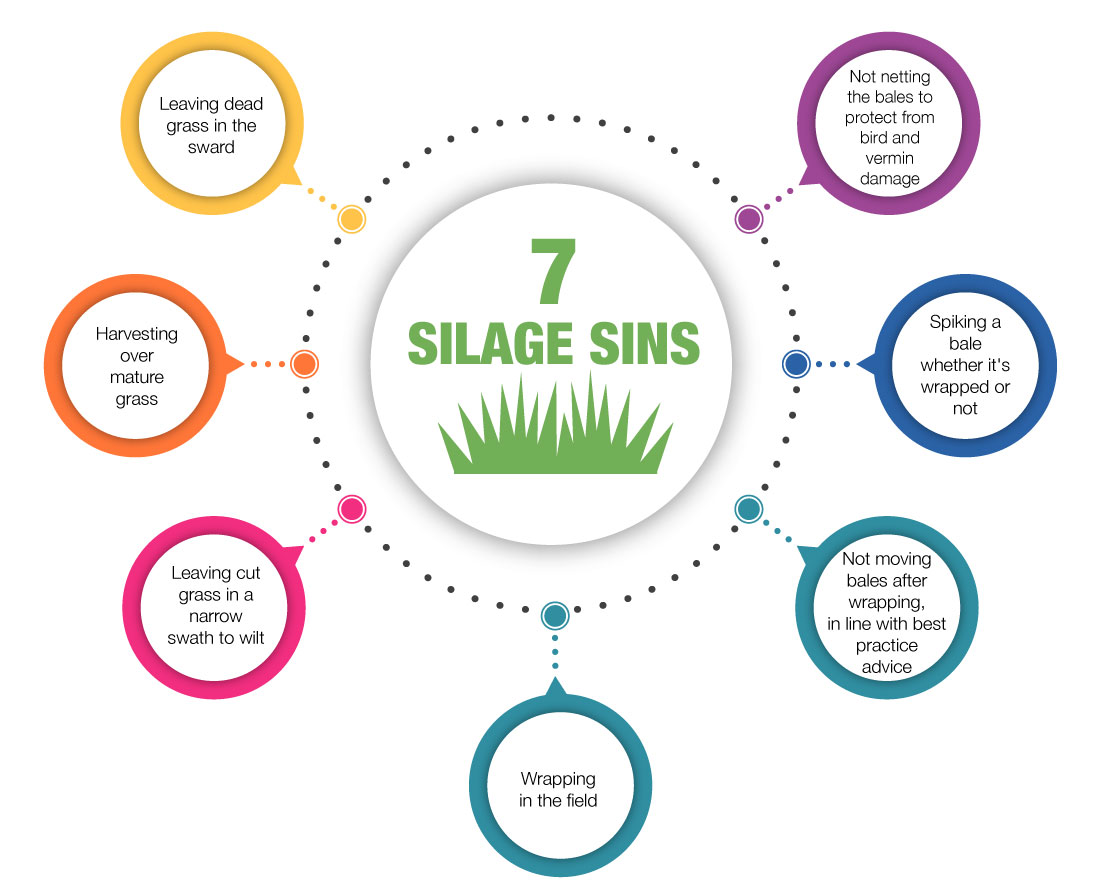

1. Leaving dead grass in the sward
Mould growth, particularly in silage bales, depends on two crucial contributory factors, says Dr. Dave Davies, a consultant at Silage Solutions Ltd and an expert in silage and rumen nutrition.
He continues:
The steps Dave is referring to start with your intended crop. Any surplus grass at the end of the previous growing season must be removed completely, preferably by grazing or failing that, by topping. If left unchecked all this material does is die and subsequently provide nutrients to support the growth of moulds and other undesirable bacteria that will remain in the sward until harvest.
Removing this surplus grass helps to reduce the number of mould propagules in the harvested sward. Surplus grass has also been shown to reduce grass growth rates in the spring and so can reduce first cut grass yields.
2. Harvesting over mature grass
Another 'sin' that can increase the likelihood of silage being contaminated by moulds is harvesting over-mature grass.
3. Leaving cut grass in a narrow swath to wilt
If you want to reduce the likelihood of mould contamination within your silage, avoid leaving your cut grass in a thick narrow swath.
Such swathes encourage mould growth because their density results in higher temperatures and humidity levels, both of which enable bacteria to thrive. In addition, thick swathes reduce the effectiveness of the wind in helping to dry the crop out.
As a rule of thumb, you should aim to spread your grass over 80 to 100% of the original harvested area (depending on ground conditions) and as soon as possible after mowing and certainly within two hours.
Doing so will promote rapid wilting and will also enable the sun to play a more active role in mould control. We all know the effects Ultra Violet radiation can have in terms of sunburn and skin cancer. Well, it's just as potent when it comes to killing undesirable bacteria and moulds in the swath.
4. Wrapping in the field
"All of the sins mentioned so far relate to things farmers should do to inhibit the presence of mould propagules in their silage bales," says Dave. "The other common mistakes are more to do with preventing oxygen ingress so that any mould that is present cannot grow.
The first of these mistakes is wrapping bales in the field. Admittedly, the advice has always been and always will be to wrap bales as quickly as possible and wrapping in the field would appear to facilitate this however doing so can present other hazards.
Read: The benefits of better bale density
Read: Advantages of Baled Grass Silage within Livestock Feeding Systems
Firstly dropping a well-wrapped bale onto the recently cut sward presents the very real risk of holes being punctured into the wrap either by stubble or by stones. When that wrapped bale is then picked up and moved to the stacking site, this damage can be exacerbated.
The advent of combi-machines in recent years means that some farmers will wrap in the field but Dave would advise that those doing so should check bales carefully for damage from stubble.
5. Not moving bales after wrapping, in line with best practice advice
It's always recommended that you move bales as quickly as possible after wrapping. This ideally means within 2 hours but where this isn't practical, you should certainly aim to move them within 8 hours. Once at the storage site, the bales should then be left in place until they're ready to be fed out
6. Spiking a bale whether it's wrapped or not
Thankfully, most of us know better than to spike a wrapped bale. However many farmers think it's OK to spike an unwrapped bale in order to move it to the wrapper. Dave Davies says these farmers need to think again.
Ultimately, this introduces so much oxygen that moulds are able to grow before the oxygen is used up after the bale has been wrapped.
As for spiking a wrapped bale?
That really is the ultimate sin. You're deliberately puncturing a film that has probably been developed and refined over the past 25 years to provide the perfect oxygen barrier and to be as thin and cost-effective as possible. Any patch used over the resulting hole will never provide the same degree of oxygen protection as the original undamaged film irrespective of how well it is applied. In short, it's always better to use a grab whenever you're moving bales - wrapped or not.
7. Not netting the bales to protect from bird and vermin damage
Having spent the time, effort and energy creating baled silage, it's hard to imagine that farmers are prepared to needlessly squander the fruits of their labours. But many do every year. Our final sin is one of the simplest of all to avoid and entails not placing a net over your bales to protect them from bird or vermin damage.
These creatures don't care that your bale wrap is there to provide an air barrier and will puncture it either with their feet whilst using the bales as a resting place or with their teeth or beak because they see the film as an obstacle between them and a potential source of food. And it's not just wild animals you need to worry about either, even the claws of your neighbour's cat can have the same negative effect.
For many, Dr Davies' advice will reflect their current bale wrapping practices. But for others, it will hopefully be an insight into the seven silage sins that they can avoid now, rather than regret later.
Please see our Disclaimer below:
We strive to ensure that the information, recommendations and guidance on the use of our products ("Product Guidance" is correct and offers the best guidance which we, or third party experts whom we have consulted, can provide to assist farmers and growers in deciding which products are suitable for your needs and getting the best results from our products. However, Product Guidance is necessarily of a general nature and cannot be tailored for the specific conditions and requirements which each farmer or grower will have. Bespoke advice on the suitability of our products and guidance on their use for your individual requirements should be obtained by contacting leominster@rpc-bpi.com. Accordingly, we make no claims, warranties, representations or guarantees on the accuracy or completeness of the Product Guidance and we exclude any legal liability or responsibility (to the maximum extent legally permissible) for the Product Guidance or for the consequences, direct or indirect, of any farmer, grower or other party following, or deciding not to follow, the Product Guidance or any part of it. Our only liability is contractual liability to purchasers of products from us as set out in our Terms and Conditions of Sale, a copy of which is available upon request from leominster@rpc-bpi.com. This disclaimer of liability applies to makingbestsilage.com, any other member of our group of companies, our officers, directors and employees, and any third party expert or other person whose materials we have included in the Product Guidance.


Contact us
Our team of experts are always on hand to help you out with any advice you may need.










